Theory: Disperse dyes are
non-ionic in nature, almost insoluble and stay as finely divided dispersed from
in water. It can be hydrolyzed in high temperature especially under alkaline
condition. Therefore dyeing with disperse dyes is virtually always done using
slightly acedia condition.
It is a unique dye staff for dyeing of polyester,
nylon and cellulose acetate fiber. These colorants have inherent affinity to
the fiber and are simply mechanically trapped in the fiber structure during
dyeing of a hydrophobic fabric contents that the fiber absorbs dye molecule,
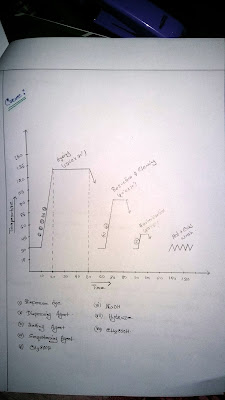
which are dissolved in the dye both.Recipe:
Disperse Dyes = 2% (owf)
Carrier = 2 g/l
Wetting agent = 1 g/l
Sequestering agent = 1 g/l
Levelling agent = 1 g/l
CH3COOH = 1 g/l
Ph = 4.5 – 5.5
Temp = 130°C
Time = 30 min
Sample weight =5 gm
Reduction & Cleaning:
NaOH = 3 g/l
Hydroze = 2 g/l
Temp = 70°C
Time = 10 min
Neutralization:
CH3COOH = 1 g/l
Temp = 50°C
Time = 10 min
Friction of the chemicalrequired:
Wetting agent: It accelerates the
wettability of material in solution thus helps to easy penetration of chemicals
into substrate. Usually it is used in scouring, bleaching & dyeing process.
It is available in market in from of yellowish liquid.
Sequestering agent: it one kind
of surface active agent act in solid liquid, solid gas or liquid
gas interfaces and reduces the interfacial tension.
Dispersing agent: using it is
used in disperse and vat dyeing process helps to distribute the dye molecules
in dye both. It is also helps to penetrate the dye molecules into the
substrate. It is available in market in powder from.
 |
| Fabric type - DIssperse Fabric Name - Polyester color - REd |
Recipe calculation:
Dye: 100 gm fabric for 2 gm dye
1
gm “ “
2/100 “
5
gm “
“ 2×5 / 100 “ = 0.1 gm
Water: 200 gm [ m:L = 1:40]
Dispersing agent , 1000 CC water, Dispersing agent required = 2 gm
1
“ “ “ =2 / 1000 “
200
“ “ “ = 2 × 200 / 1000 gm = 0.4g
Wetting agent , 1000 CC water, wetting agent required = 1 gm
1
“ “ “ =1 / 1000 “
200
“ “ “ = 1× 200 / 1000 gm = 0.2g
Similarity,
Sequestering agent = 0.2 g/l
Levelling agent = 0.2 g/l
CH3COOH = 0.2 g/l
NaOH = 0.6 gm
Hydroze = 0.4 gm
Neutralization:
CH3COOH = 0.2 g/l
Conclusion: The addition of
dispersing agent increase the dye solubility and accelerate the dye diffusion
into the swelled fiber structure. The dye diffusion can be detained either.
Using a suitable currier or providing high temperature and pressure.
how cloth dye in india
No comments:
Post a Comment