Theory: Reactive dye reach with fabric in presence of alkali
and adheres as a part of the fiber. Three principle steps are happened during
reaction dyeing. Exhaustion or reaction and after treatment as washing when a
cellulosic fibre is immersed into dye solution; negative charge produce and
surrounded the fiber.
On the other band the reactive dyes produce negative
charge into dye both, thus a repulsion force occurred. Use of electrotypes
neutralizes the negative surface charge of the fiber. Due to affinity of the
reactive dye to the fiber acidity the dye molecules move forward to the surface
of the fiber. Thus phase of dyeing is called absorption. Then the dye molecules
diffused into the swelled fiber structure through fiber pores and distribute
over the fib. This step is called exhaustion.Recipe:
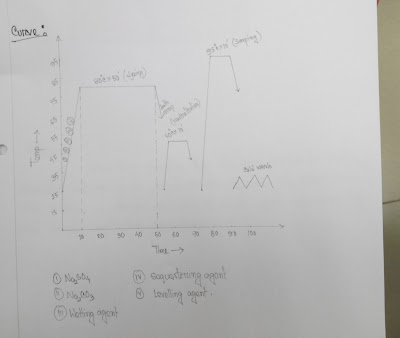
Dyes = 3%
Glober salt (Na2SO4) = 60 g/l
Soda (NA2CO3) = 20 g/l
Wetting agent = 1 g/l
Sequestering agent = 1 g/l
Levelling agent = 1 g/l
Temp = 80°C
Time = 50 min
Sample weight =5 gm
Neutralization:
CH3COOH = 1 g/l
Temp = 50°C
Time = 10 min
Soaping:
Detergent = 1 g/l
Time = 10 min
Temp = 95 °C
Friction of the chemical required:
Wetting agent: It accelerates the wettability of material in
solution thus helps to easy penetration of chemicals into substrate.
Sequestering agent: it one kind of surfactants surface
active agent act in solid liquid , solid gas or liquid gas interfaces and
reduces the interfacial tension.
Levelling agent: Levelling agent is used in textile
coloration process to active uniform dyeing over whole substrate by controlling
the rate of dyeing.
Electrolytes: Use of electrolytes neutralizes the negative
surface charge of fiber.
Recipe calculation:
Dye: 100 gm fabric for
3 gm dye
1 gm
“ “ 3/100 “
5 gm
“ “ 3×5 / 100 “ = 0.15 gm
Water: 200 gm [ m:L = 1:40]
Na2SO4 = 1000 CC water, NA2CO required = 60 gm
1 “ “ “ =60 / 1000 “
200 “ “ “ = 60 × 200 / 1000 gm = 12g
Similarity,
NA2CO3
= 4 g/l
Wetting agent = 0.2 g/l
Sequestering agent = 0.2 g/l
Levelling agent = 0.2 g/l
CH3COOH = 0.2 g/l
Detergent = 0.2 g/l
Conclusion: Now-a day reactive dyes are very popular for
textile coloration because of its some specific properties like color fastness
wide range of shad, brilliance of shade , good reproducibility and simple
application procedure.

Discover the ultimate solution for accurate moisture analysis in textiles with our Textile Moisture Meter.
ReplyDeletethank you!!
Wow, I came to learn about machines, and your information is absolutely amazing! For more insights and if your are looking for the Lockstitch Sewing Machines
ReplyDelete! we provide high-speed Lockstitch Sewing Machines with eco-friendly motors and technical support !