Theory: azoic dye are not ready
mode dyes like reactive dyes. The insoluble azoic colors are synthesized inside
the fiber by coupling of two individual components neither of which is a dye
itself. These two components are on aromatic diezoniem
solt and an aromatic
hydroxyl compound. After diazotization the actual color is developed in the
substrate. In application of azoic colors, the first step is selecting the west
suitable diazo and coupling components combination of a particular purpose is
to decide which of the napthols can be used in conjunction with the available
diazo components to give the color closest to the chemical shade and depth. |
| Fabric type : Cotton Dye type : Azoic Color : Orange |
Recipe:
1st step
Naptholation:
napthol = 2% (owf)
NaOH = 3 g/l
NaCl = 5 g/l
Wetting agent = 1 g/l
Sequestering agent = 1 g/l
Levelling agent = 1 g/l
Ph = 10
Temp = 30°C
Time = 15 min
Sample weight =5 gm
Base = 2% (owf)
CH3COONa= 2 g/l
HCL = 2 g/l
NaNO2 = 2 g/l
Wetting agent = 0.5 g/l
Sequestering agent = 1 g/l
Levelling agent = 1 g/l
Temp = 5°C
Time = 15 min
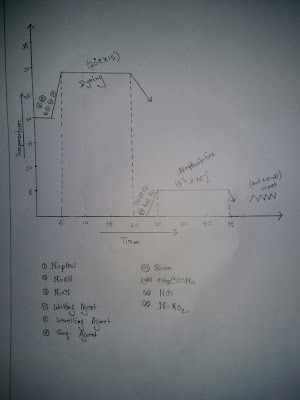
Curve For Azoic dye
 |
| Curve For Azoic dye |
Wetting agent:
It accelerates the
wettability of material in solution thus helps to easy penetration of chemicals
into substrate. Usually it is used in scouring, bleaching & dyeing process.
It is available in market in from of yellowish liquid.
Sequestering agent:
it one kind
of surfactants surface active agent act in solid liquid, solid gas or liquid
gas interfaces and reduces the interfacial tension.
Recipe calculation:
Dye: 100 gm fabric for 2 gm naphthol
1
gm “ “
2/100 “
5
gm “
“ 2×5 / 100 “ = 0.1 gm
Water: 200 gm [ m:L = 1:40]
NaOH , 1000
CC water, Carrier required =
3 gm
1 “ “ “ =3 / 1000 “
200 “ “ “ = 3 × 200 / 1000 gm = 0.6g
Similarity,
NaCL = 1 gm
Wetting agent = 0.2 g/l
Sequestering agent = 0.2 g/l
Levelling agent = 0.2 gm
2nd process:
Dye: 100 gm fabric for 2 gm base dye
1
gm “ “
2/100 “
5
gm “ “
2×5 / 100 “ = 0.1 gm
Water: 200 gm [ m:L = 1:40]
NaOH ,
1000 CC water CH3COONa required = 2 gm
1 “ “ “ =2 / 1000 “
200 “ “ “ = 2 × 200 / 1000 gm = 0.4g
Similarity,
HCL = 0.4 gm
NaNO2 = 0.4 gm
Wetting agent = 0.1 g/l
Sequestering agent = 0.2 g/l
Levelling agent = 0.2 gm
Conclusion: Azoic dye are
commonly used for dyeing of cotton although other cellulose fibers, wool and
even some synthetic fiber as well the main advantage of this dyes is that
produce an economical way to abtain certain shade especially red with very good
wash fastness.
No comments:
Post a Comment